
teams with optimisation do not play nice with e164 addressing – that is to say for the teams direct optimisation to work we need a e164 adress for hosts that in the site subnet
i am a bit pressed for time – but this is the problem when you deploy the e1 you may size it for growth and get it wrong- resulting in maybe some PBX based routing and some internal extensions which dont immediatly translate into a true e164 address
but how do you find them and know you got them the first way would be a simple extension count if you got more endpoints than DDIs in your e1 circuit then a PBX designer has got clever with the dial plan
The phone number mask trick
This allows you to make a call from an internal number by using a mask that is in the public DDI range. This means the E1 circuit will accept it but you cannot ring it back but you could use an IVR to redirect to the internal range for inbound

best way to tackle this is with some SQL
run sql select dnorpattern, d.description, e164mask, tkpatternusage from devicenumplanmap inner join numplan on fknumplan=numplan.pkid join device d on fkdevice = d.pkid where e164mask= “+52867711XXXX”
choose your mask against Publice DDI ranges if you got extensions in this range that dont trannslate
The SBC outbound source trick
This just makes the manipulation for the public range at the SBC
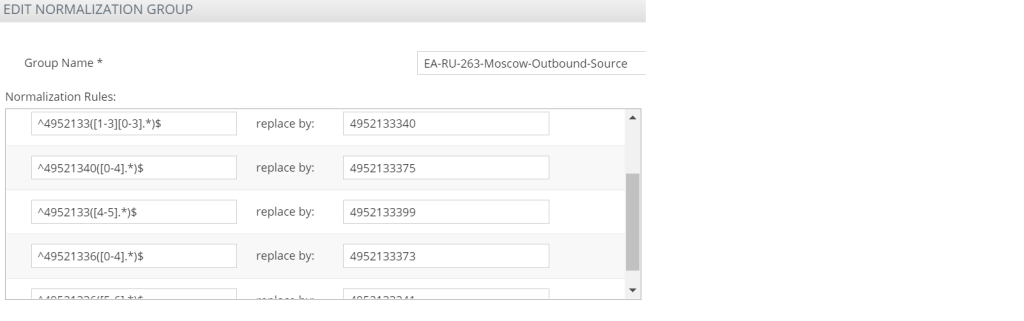
its doing the same thing we are normalising to a public number – this would be good for contact centre routing instead of making them non dialable by some other means
Testing Direct Media optimisation

For direct media optimisation to work we need ;
- subnet , to punch the media to from the internal sip interface to the site E1
- It aslo must see VPN addresses as a site address
- Calls from the public internet are external calls
- The WebRTC element must work for both
- The media must be encypted
- Call forwarding and other re directions must be supported
- we got to able to transfer
- we got to eb able to hold snd retrieve
- Internal IP streams flow via Internal SBC sip interfaces
- External IP streams flow via external SBC SIP interfaces
so in its way this defines a test list
Dump SBCs in the environment
Get-CsOnlinePSTNGateway is going to dump all the PSTN gateways – which are configured to allow the internet reach voice networks – they are a list of SBC SIP interfaces
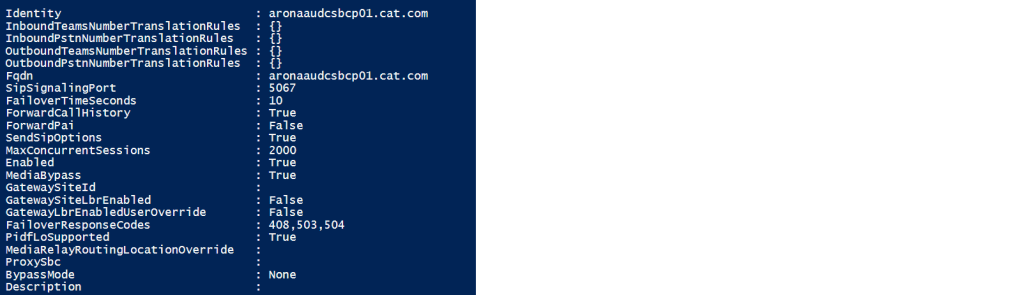
The site E1 SBC looks like this
Identity : mybiz.com
InboundTeamsNumberTranslationRules : {}
InboundPstnNumberTranslationRules : {}
OutboundTeamsNumberTranslationRules : {}
OutboundPstnNumberTranslationRules : {}
Fqdn : mybiz.com
SipSignalingPort : 5067
FailoverTimeSeconds : 10
ForwardCallHistory : True
ForwardPai : False
SendSipOptions : True
MaxConcurrentSessions : 1000
Enabled : True
MediaBypass : True
GatewaySiteId : Gateway ID
GatewaySiteLbrEnabled : False
GatewayLbrEnabledUserOverride : False
FailoverResponseCodes : 408,503,504
PidfLoSupported : False
MediaRelayRoutingLocationOverride :
ProxySbc : Teams Voice proxy
BypassMode : Always
Description :
when you configure a test account
RunspaceId : 56be03ea-2ddc-4f15-be4c-5b40a051b355
Identity : [email protected]
SipAddress : sip:[email protected]
ServiceNumber :
TollFreeServiceNumber :
ConferenceId : 0
BridgeId : 4bb5ceda-d994-4121-a671-44d92ffda798
BridgeName : Conference Bridge
Tenant : ceb177bf-013b-49ab-8a9c-4abce32afc1e
AllowPstnOnlyMeetings : False
AllowTollFreeDialIn : False
LeaderPin : *
UserPrincipalName : [email protected]
HostedVoiceMail : True
EnterpriseVoiceEnabled : True
OnPremLineURI : tel:+78126482513
OnlineVoiceRoutingPolicy : 402-Tosno-Users
TeamsCallingPolicy : AllowCalling
Troubleshooting Inbound DMO at the SBC

There are a few global truths – if we have an M800 with with an E1 – than that is the resource we want to control at a site based SBC – i mean we could by means of manipulating call number masks and ARM ( brain ) maybe exit via one SBC and enter by another – this is acceptable in the SBC verse and i will test this later but here we want to control what the site based E1 can do via the SBC – so before we brought a SIP interface into the SBC – this would of meant we manipulate in the Brain – and its slave army of SBC’s but if we need to manaipulate we can do it in the gateway
when we have a telephony resource in a gateway we can punch media through to the e1 via the SBC to GW interface that i think got mentioned in the m800 set up thread
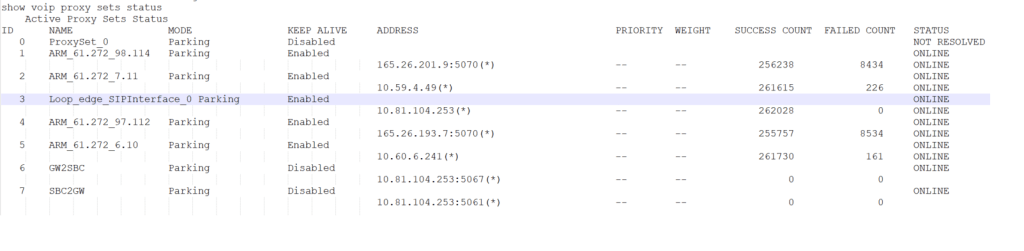
the GW to SBC interface passes back the ISDN signalling back to the SBC when the communication has to go the other way the IP group for GW2SBC is shown below
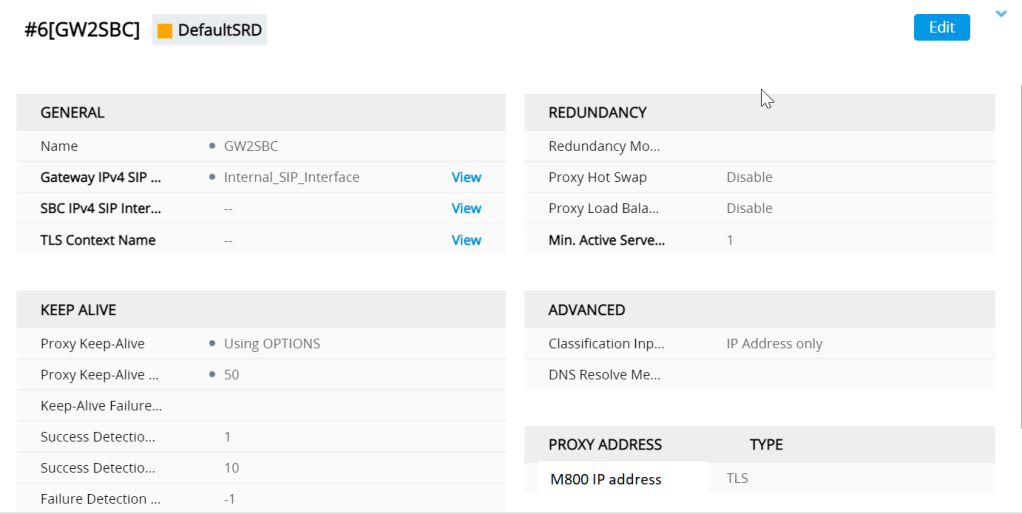
The IP group looks like
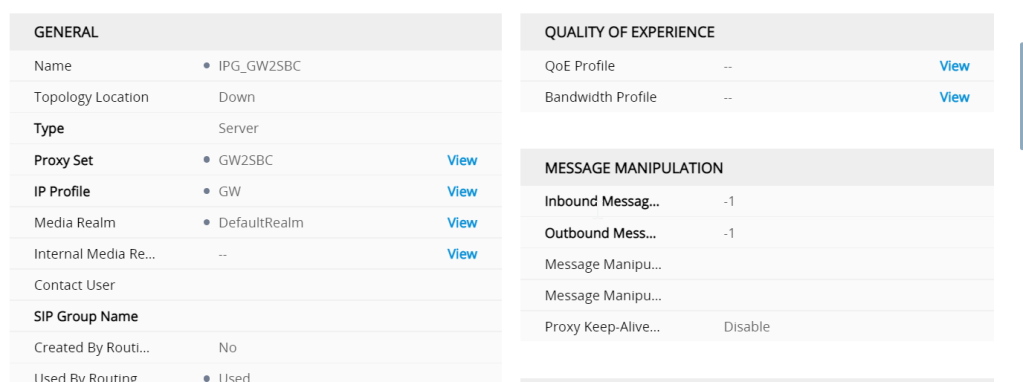
One of the most imortant settings here is the used by routing server setting (ARM) without this it wont work
classified by proxy this feels like a control
whats is classification ?
Classification is the process in which the AudioCodes gateway or SBC uses to associate the source of a SIP dialog request with a IP Group. By associating the source of the call with a defined IP Group entity, the SBC can then use this association to determine how the call will be processed. The classification rules cannot only be used to define the source of the SIP request for routing/manipulation purposes, but it canalso be used to block unwanted call attempts.
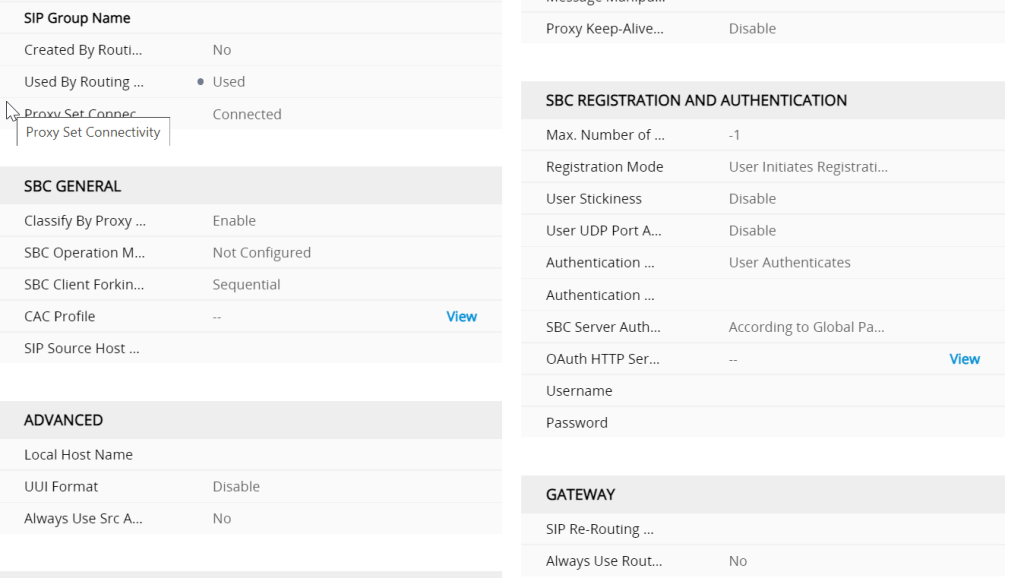
How does AudioCodes classify incoming calls?
AudioCodes uses three stages when attempting to classify an incoming SIP dialog request.
- The first stage is to attempt to classify the SIP dialog by first comparing if the source of the
request already exists in the device’s registration database. - If the device is not found in the AOR/registration database, the source can then be compared
against the defined IP Address/ports used in the ProxySets table. If the source is found to be a match with
one of the defined ProxySet entries, the call will be then associated with the source IPGroup which uses
that ProxySet. This option can be enabled through the “Classify by Proxy Set” definition found in the
IPGroup table definition. - Finally, if the call does not match either the registration database or the definitions in the
ProxySet table, the AudioCodes device will attempt to match the source by comparing the SIP request
with the criteria defined in the Classification Table.
Are some classification options better than others?
For security purposes, it is recommended to use the Classification rules as defined in the Classification
Table, as the Classification Rules allows the user to define additional SIP message characteristics that can be used to increase the strictness and security of the classification process. Classifying the SIP request source by the Proxy Set is allowed but is only recommended if the IP address of the IP Group is unknown or is configured with a FQDN.
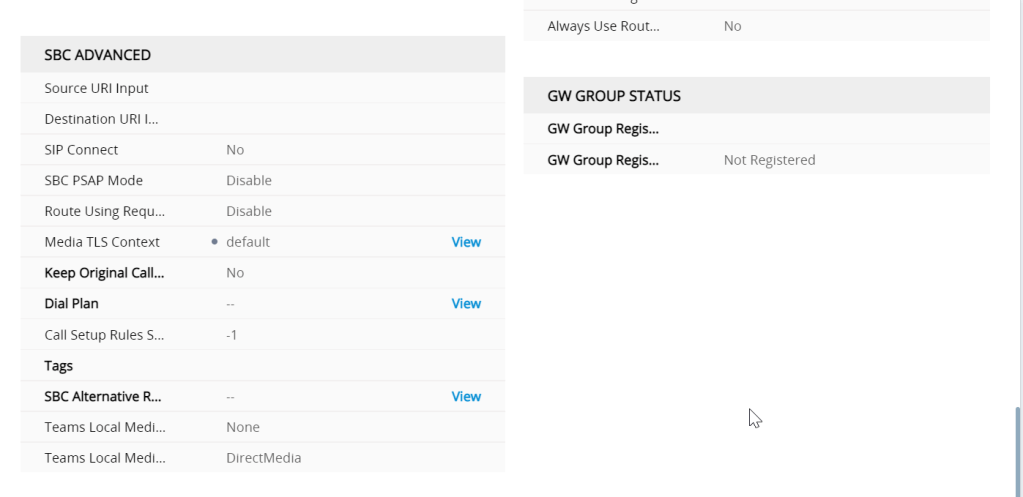
SIP interfaces
covered in other parts of the blog but i am going to do a quick primer here
the Internal SIP is the GW application and the SBC interface is for the SBC (application type)
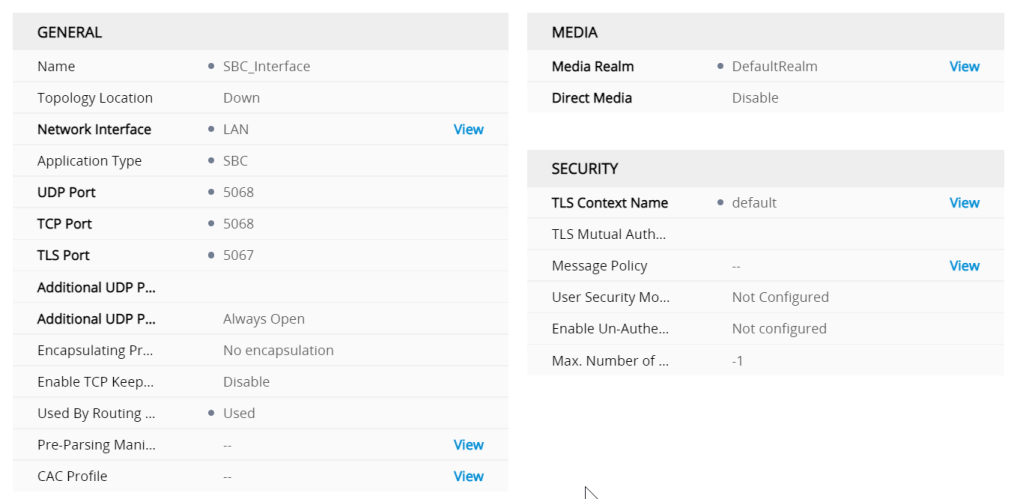
the proxy set and IP groups defines the signalling interfaces and ports needed to go from GW to SBC and SBC back to GW to punch the media back to the E1
Though the actual properties of an interface is defined in the profile , if there are tweaks to be made to get something to work the profile seesm to be the place
ARM basically controls the profile back to the regional and the GW controls the E1
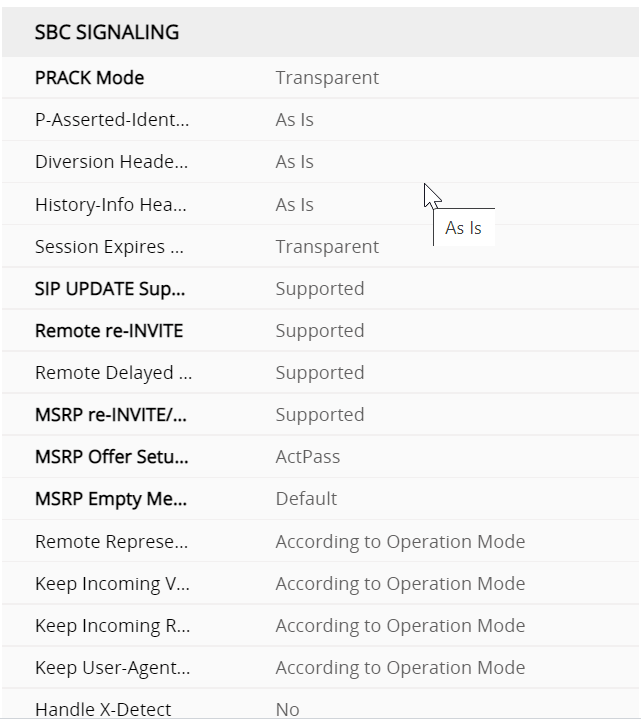
IP profiles are quite meaty configs Regional ARM profile
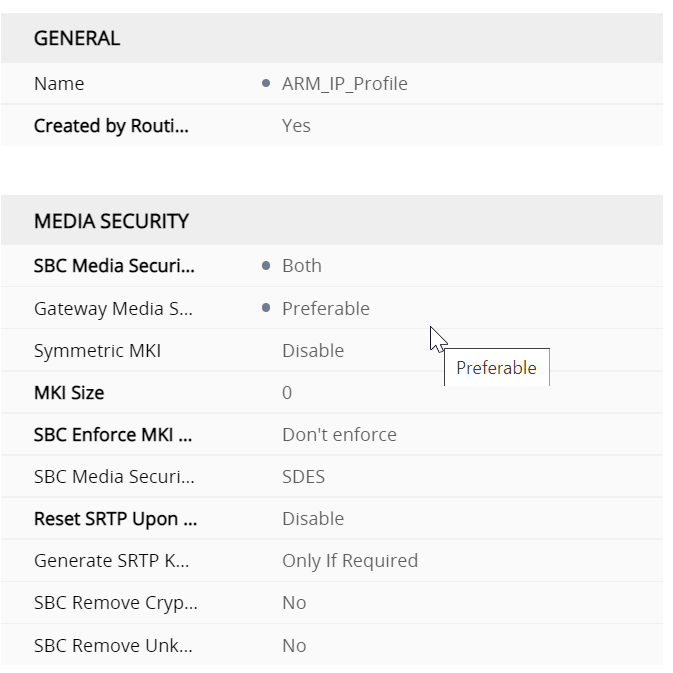
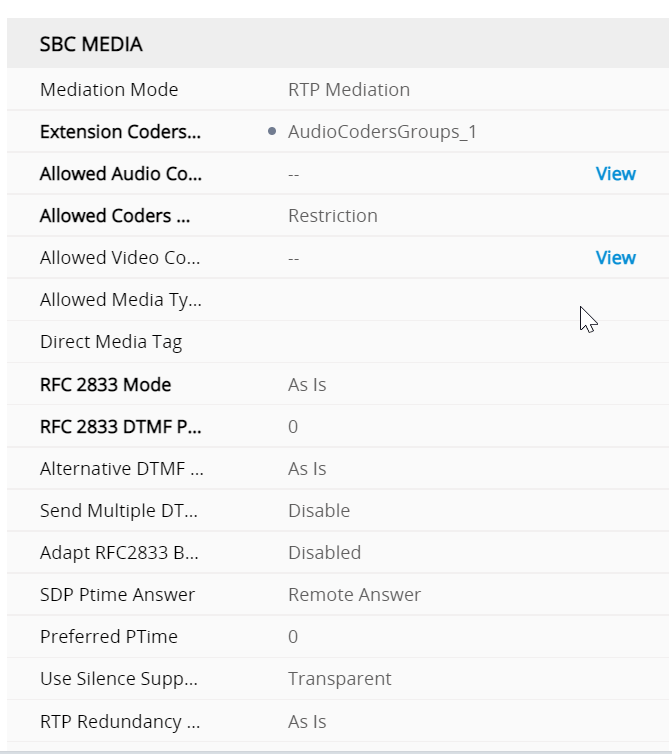
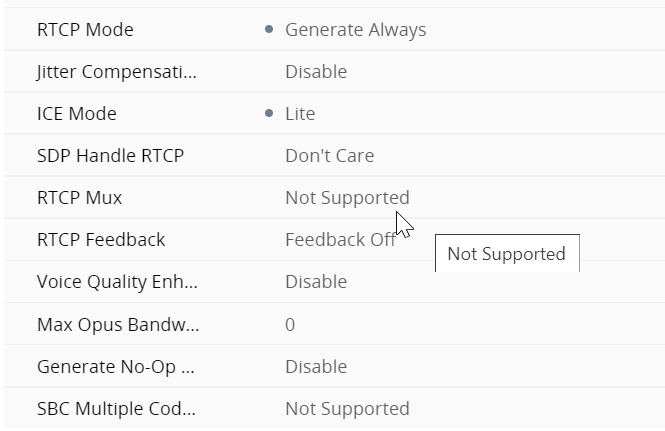
SBC signalling ARM profile regional
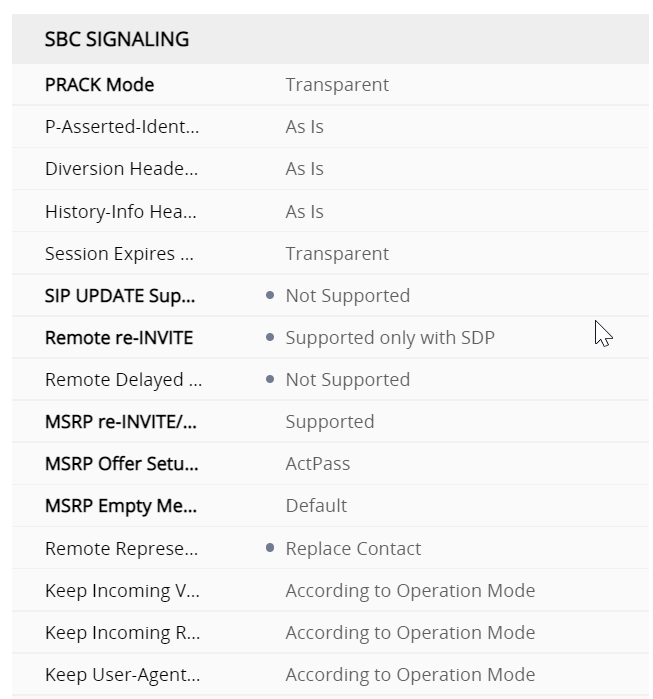
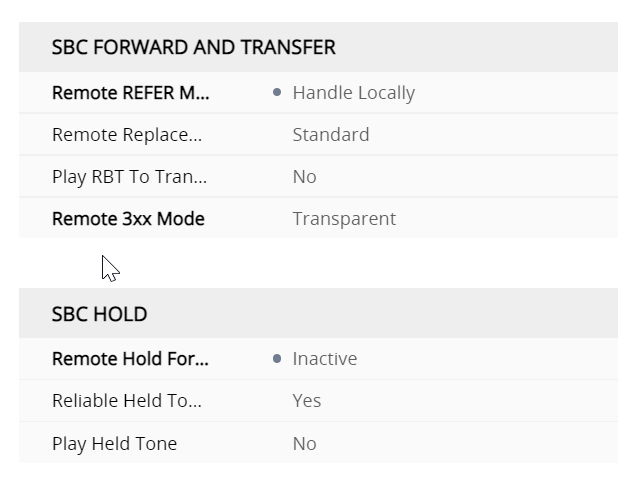
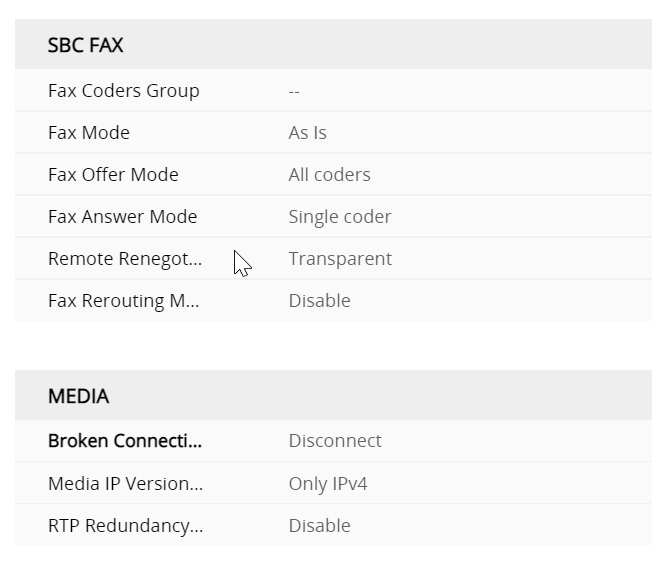
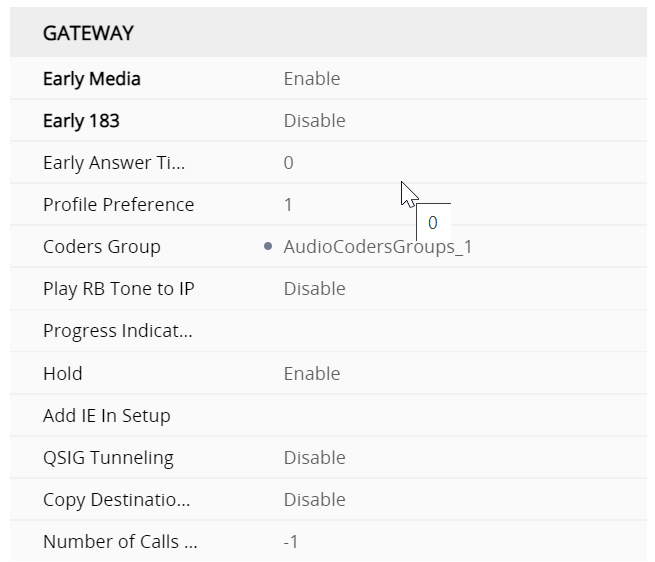
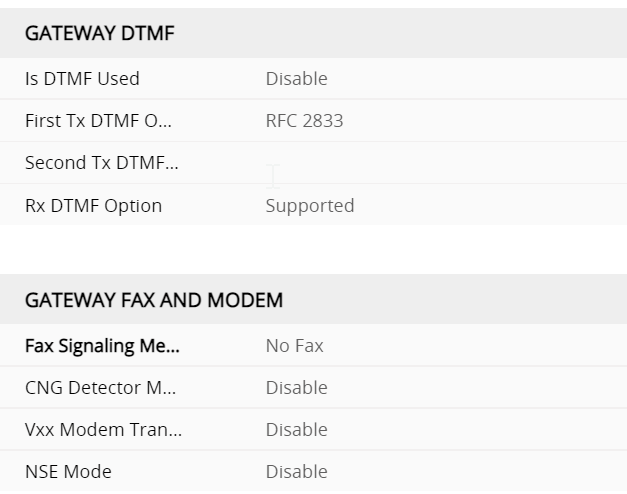
so whats the Profile for the GW interface look like
so whats the profile for the gateway look like ?
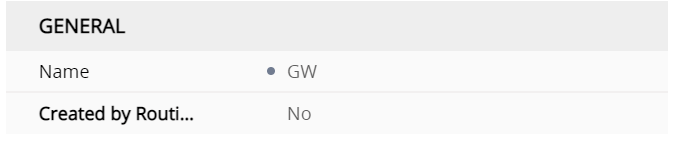
The first difference is that it isnt created by the routing server
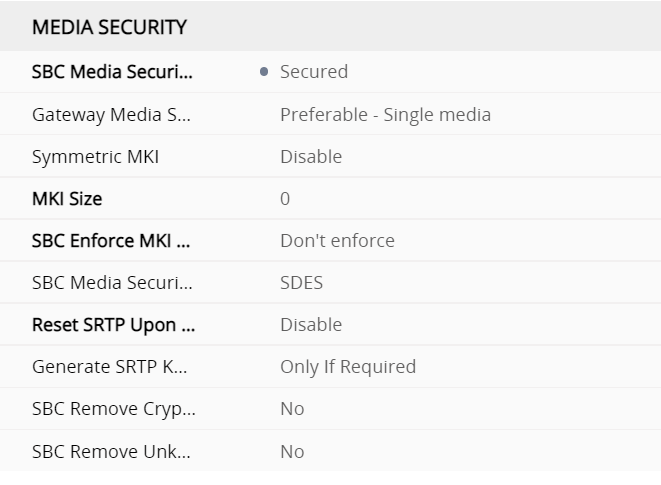
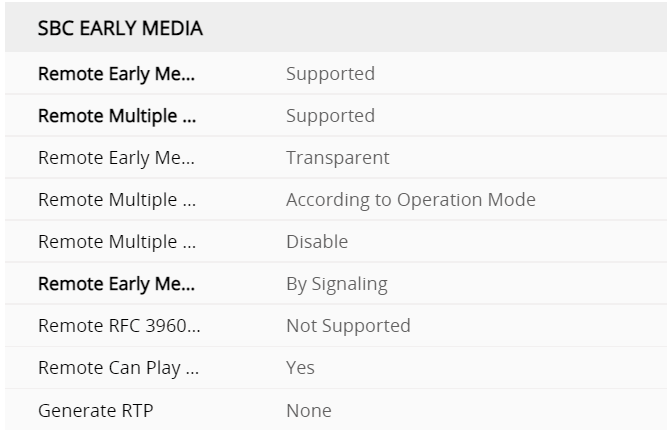
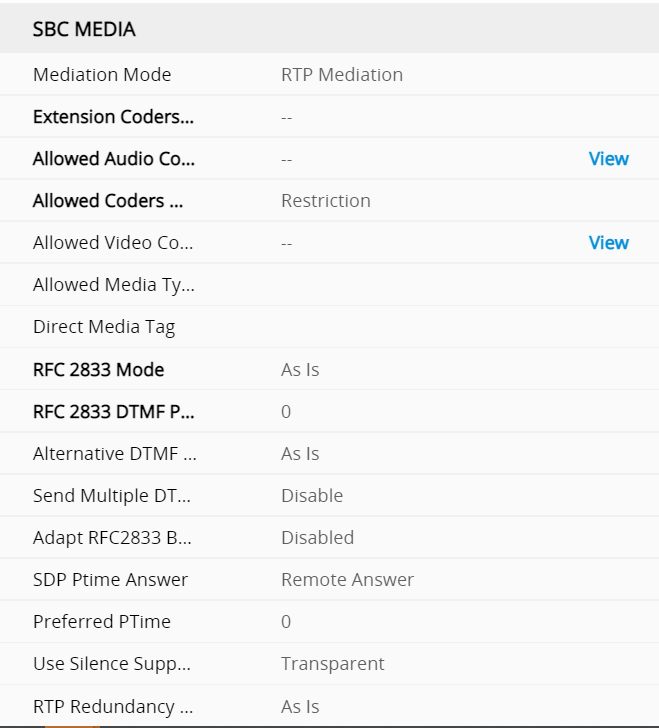
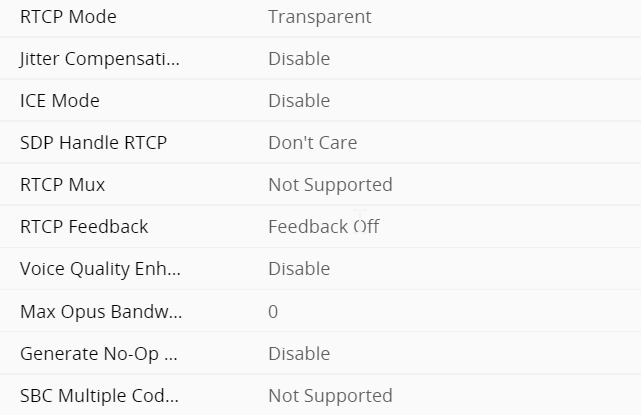
Gateway Profile SBC signalling M800
under the profiles this defines what gets translated from the SBC interface to the gateway
Desiging DMO SBC routing environments
This comes down to good IP management i mean , the bible is here
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftteams/direct-routing-media-optimization-configure
the first big takeaway is this
External trusted IPs are the Internet external IPs of the enterprise network. These IP’s are the IP addresses used by Microsoft Teams clients when they connect to Microsoft 365. You need to add these external IPs for each site where you have users using Local Media Optimization.
so this should be an easy check by using a get instead
Get-CsTenantTrustedIPAddress
what you get is a list of
Identity : 10.0.0.2
MaskBits : 32
Description : Site Description
IPAddress : 10.0.0.2
Identity : 65.26.78.98
MaskBits : 32
Description : site description
IPAddress : 65.26.78.98
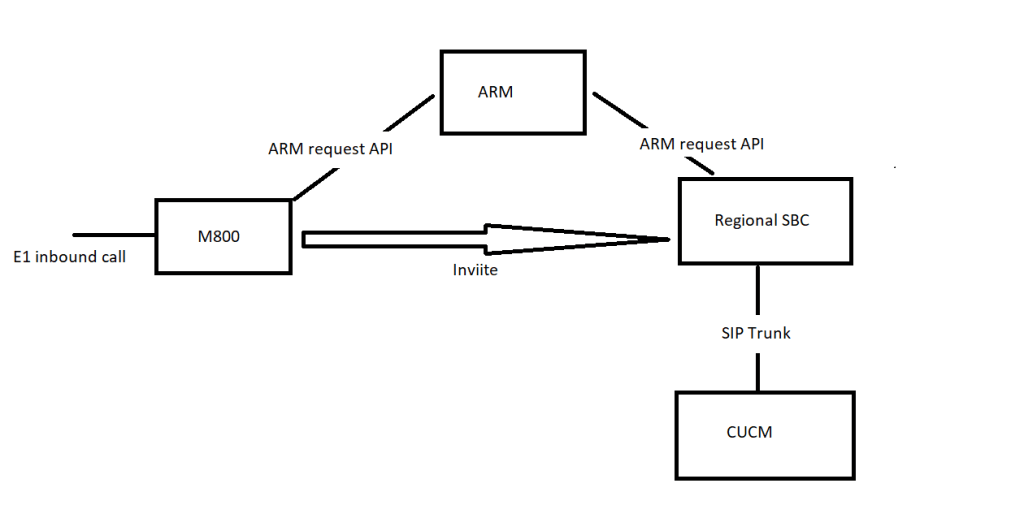
basically we got to see a PSTN event – in this architcture we invite the reginonal but any 200OK has got to point back to the M800 SBC to GW interface
Also worth mentioning that this is for a hybrid environment where we have a regional SIP trunk per region where we interwork with a PBX
when we have a fully migrated user – there wouldnt be an invite to the regional
let see what the PSTN say
